What is a temperature sensor?
A temperature sensor is a device that measures and reports temperature. It translates thermal data into electrical signals, enabling precise monitoring of environments or substances. These sensors are vital in various applications, from industrial processes to household appliances, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
How Temperature Sensors Can Improve Restaurant's Food Safety
Smart Temperature Monitoring
In the world of the restaurant industry, ensuring food safety is paramount. One critical aspect of maintaining food safety standards is temperature control. Traditionally, this has involved manual methods of temperature monitoring, which, while foundational, have limitations in accuracy, efficiency, and consistency.
Traditional temperature monitoring in restaurants usually relies on handheld thermometers, which require staff to manually check and log the temperatures of various food items and storage environments. This process typically involves probing different sections of stored foods, like meats, dairy, and produce, to ensure they are stored at safe temperatures. For hot food, this might mean ensuring temperatures are high enough to prevent bacterial growth, while for cold storage, the focus is on maintaining temperatures low enough to preserve freshness and prevent spoilage.
However, these manual checks are subject to human error. Inaccurate readings can occur due to improper use of thermometers or irregular monitoring schedules. Moreover, manual logging of temperatures, often done on paper charts or basic digital records, can be tedious and prone to inaccuracies or omissions. This method also doesn't provide real-time alerts or continuous monitoring, which means that temperature fluctuations might go unnoticed until the next scheduled check, potentially leading to food safety hazards.
In contrast, smart temperature monitoring represents a significant leap forward. Utilizing advanced sensor technology, these systems offer continuous, real-time monitoring of food and storage temperatures. This means that restaurant staff can be immediately alerted to any deviations from the set safe temperature ranges, allowing for quick corrective action. This is especially crucial in a busy restaurant environment where attention can be stretched across multiple tasks.
Smart temperature sensors not only provide more accurate and consistent readings but also automate the recording process. This automated data logging ensures a more reliable and hassle-free compliance with health regulations, as it provides a detailed, timestamped record of temperature readings without manual input.
As the industry evolves, the move towards smart temperature monitoring systems is becoming increasingly essential. By integrating these advanced technologies, restaurants can enhance food safety, reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses, and streamline their operations, ultimately leading to better customer satisfaction and business success.
The Importance of Temperature Control in Food Safety
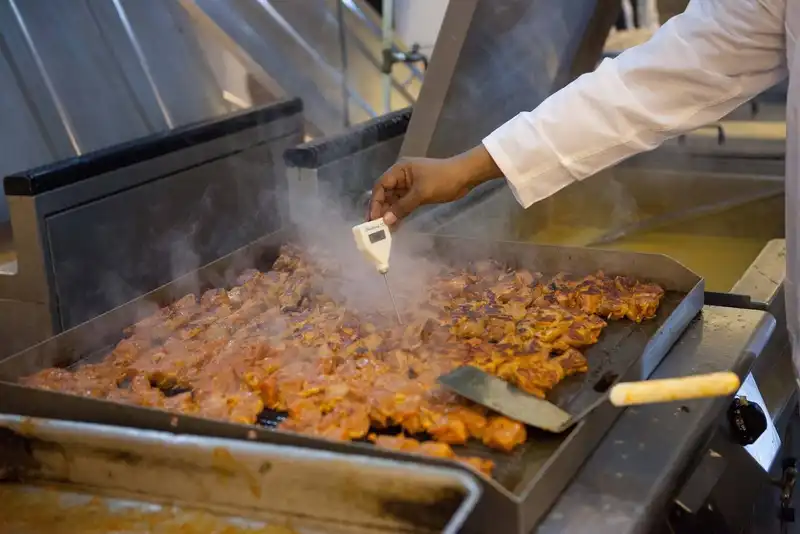

Temperature control is a cornerstone of food safety in the restaurant industry. It plays a vital role in preventing foodborne illnesses, ensuring that food is safe for consumption. Understanding and adhering to this aspect of food safety is not just a best practice but a necessity, underpinned by strict regulatory standards.
Foodborne illnesses are a significant public health concern, caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites, or chemical substances entering the body through contaminated food. One of the most effective ways to prevent the growth and spread of harmful microorganisms in food is by controlling its temperature. Microorganisms such as bacteria typically thrive in what is known as the 'danger zone,' a temperature range between 40F and 140F (4C and 60C). In this range, bacteria can double in number in as little as 20 minutes, turning seemingly safe food into a health hazard.
To mitigate this risk, temperature control involves maintaining cold foods at temperatures below 40F and hot foods above 140F. This is critical at all stages of food handling, from receiving and storage to preparation and serving. In refrigerators, temperatures must be low enough to slow bacterial growth, while cooking temperatures should be high enough to kill any present bacteria. Similarly, during the serving and display of food, maintaining the right temperature ensures that the food remains safe to eat over time.
Regulatory bodies around the world have established strict standards for food temperature control to ensure public safety. In the United States, for example, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) sets out guidelines in the Food Code, which many state and local health departments adopt. These standards provide detailed requirements for different types of food, outlining specific temperatures and times for cooking, reheating, cooling, and storing.
Compliance with these regulations is not merely about avoiding legal repercussions; it's about ensuring customer safety and maintaining a restaurant's reputation. Regular health inspections check for adherence to these standards, and failure to comply can result in fines, closure of the establishment, or, worse, a foodborne illness outbreak traced back to the restaurant.
Temperature control also extends beyond bacterial prevention. It plays a role in preserving the quality and taste of food. Proper temperature management ensures that food retains its intended flavor, texture, and appearance, contributing to the overall dining experience.
For restaurant owners, understanding the critical role of temperature in preventing foodborne illnesses is essential. It requires a commitment to rigorous training for staff, investment in the right equipment, and diligent monitoring and record-keeping. By prioritizing temperature control, restaurants not only comply with health regulations but also demonstrate a commitment to the well-being of their customers, which is invaluable for building trust and loyalty in the competitive food industry.
Create, Implement, and Execute Multiple Daily Checklists
Streamline Your Operations with Altametrics
Understanding Temperature Sensors
In the modern culinary world, smart temperature sensors have become an integral component of food safety and quality management in restaurants. Understanding these devices, their functionality, and their various types is essential for restaurant owners and managers aiming to maintain high standards of food safety.
Smart temperature sensors are advanced devices designed to measure and report temperature data accurately and consistently. Unlike traditional thermometers that require manual reading and recording, smart sensors automate these processes, offering real-time monitoring and data logging. These sensors work by converting temperature into a readable digital format, often transmitting this data wirelessly for easy access and analysis. The integration of these sensors into restaurant operations signifies a shift towards more efficient, precise, and reliable temperature control, crucial for food safety.
One notable innovation in this field is the Wifi thermometer. These thermometers connect to a restaurant's Wi-Fi network, allowing for remote monitoring of temperatures. This means that restaurant staff can track temperature readings of refrigerators, freezers, and cooking appliances from a centralized dashboard, often accessible via smartphones or computers. The ability to monitor these temperatures in real-time and receive instant alerts if temperatures deviate from the set safe range is invaluable. It not only ensures immediate response to potential food safety risks but also adds a layer of convenience and efficiency, freeing staff from the need for constant manual checks.
There are several types of smart temperature sensors, each suited for different applications in a restaurant setting. Some of these include.
1. Probe Thermometers - Essential for checking the internal temperature of cooked foods, particularly meats, to ensure they have reached safe temperatures.
2. Infrared Thermometers - These allow for non-contact surface temperature readings, useful for checking the temperature of food on buffet lines or cooking surfaces.
3. Data Loggers - Often used in storage areas, these devices record temperature over time, providing a comprehensive view of temperature trends and aiding in identifying any inconsistencies.
4. Automated Temperature Monitoring Systems - These systems consist of multiple sensors placed throughout the restaurant, providing a holistic approach to temperature monitoring. They are particularly useful in large establishments where manual monitoring would be time-consuming and potentially unreliable.
Each type of sensor serves a specific purpose, from ensuring the correct cooking temperature of foods to maintaining the ideal storage conditions. Selecting the right combination of sensors can significantly enhance a restaurant's ability to maintain consistent food safety standards.
Moreover, the evolution of temperature sensors towards smarter, more connected solutions like Wi-Fi thermometers represents a significant leap forward in food safety technology. By harnessing these tools, restaurants can not only meet the stringent demands of food safety regulations but also optimize their operations for better efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Advantages of Smart Temperature Sensors
In the dynamic environment of a restaurant, maintaining optimal food safety standards is a constant challenge. One of the key factors in this battle is effective temperature control. With the advent of smart temperature sensors, the landscape of temperature monitoring in the restaurant industry has seen a significant shift, offering numerous advantages over traditional methods.
Traditional temperature monitoring methods typically involve manual thermometers that require staff to physically check and record temperatures at various points throughout the day. This process, while fundamental, is fraught with the potential for human error and inconsistencies. Manual readings can vary depending on the skill and diligence of the staff, and maintaining accurate logs can be a cumbersome task. Moreover, these methods do not provide continuous monitoring, which means that fluctuations in temperatures, particularly critical in areas like refrigerator temperatures, might go unnoticed for hours, potentially compromising food safety.
Smart temperature sensors, on the other hand, bring a high level of precision, efficiency, and real-time monitoring capabilities to the table. These advanced devices automate the temperature monitoring process, providing continuous, accurate readings of refrigerator temperatures and other critical points in the food storage and preparation areas. This continuous monitoring is crucial for ensuring that food is stored safely and that any deviations from the required temperature ranges are quickly detected and addressed.
One of the most significant advantages of smart sensors is their accuracy. Unlike manual methods, where readings can be subject to human error, smart sensors provide precise and consistent temperature data. This level of accuracy is essential for complying with stringent food safety standards and for ensuring the quality and safety of the food served to customers.
Efficiency is another key benefit of these sensors. Automated temperature monitoring frees up staff from the time-consuming task of manual checks, allowing them to focus on other critical aspects of restaurant operations. Additionally, the data collected by smart sensors can often be accessed remotely, meaning that restaurant managers can monitor temperatures from anywhere, at any time, ensuring peace of mind and the ability to respond quickly to any issues.
The real-time monitoring capability of smart sensors is a necessity. Traditional methods only provide a snapshot of the temperature at the time of the reading, but smart sensors offer a continuous stream of data. This means that any unexpected changes in temperature, such as a refrigerator failing overnight, can be immediately detected and addressed, potentially saving thousands of dollars in spoiled food and preventing foodborne illnesses.
Integrating Smart Sensors into Your Restaurant Operations
Integrating smart temperature sensors into restaurant operations is a strategic move towards enhancing food safety and operational efficiency. This integration involves a series of steps and considerations to ensure that the technology aligns seamlessly with existing systems and procedures.
Step-by-Step Guide for Integration
1. Assessing Needs and Planning
Begin by assessing the specific needs of your restaurant. Identify critical points where temperature monitoring is essential, such as refrigerators, freezers, storage areas, and cooking stations. Plan the type and number of sensors needed for each area.
2. Choosing the Right Sensors
Select sensors based on your specific requirements. Consider factors like range, accuracy, connectivity options (such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth), and compatibility with existing systems. For instance, a Wi-Fi-enabled temp alert system can provide real-time notifications in case of temperature deviations.
3. Installation and Setup
Install the sensors following the manufacturer's guidelines. This typically involves placing sensors in strategic locations where they can accurately measure temperatures without being obstructed. Ensure that sensors in refrigerators and freezers are positioned to provide representative readings of stored food temperatures.
4. Connecting to a Network
Connect the sensors to your restaurant's Wi-Fi network or other communication systems. This connection is crucial for transmitting data to the central monitoring system or dashboard.
5. Configuring Alerts and Thresholds
Configure the temp alert thresholds according to the safe temperature ranges for different foods and storage conditions. Set up alerts to notify staff via email, SMS, or app notifications when temperatures fall outside these ranges.
6. Integrating with Existing Systems
Integrate the temperature monitoring system with your existing restaurant management software. This integration can streamline operations by linking temperature data with inventory management, compliance reporting, and other operational aspects.
7. Training Staff
Train your staff on how to interpret sensor readings and respond to alerts. Ensure they understand the importance of temperature control and the role of smart sensors in maintaining food safety.
8. Regular Maintenance and Calibration
Schedule regular maintenance and calibration of sensors to ensure ongoing accuracy. This might involve periodic checks and adjustments by a professional technician.
Tips for Seamless Integration
Customization - Customize alerts and reports to meet the specific needs of your restaurant, like different settings for daytime and nighttime or specific days of the week.
Data Utilization - Utilize the data collected for continuous improvement in food safety practices, such as identifying recurring issues or optimizing food storage arrangements.
Ensuring Connectivity - Maintain robust Wi-Fi or network connectivity to ensure uninterrupted data transmission and alert systems.
Feedback Loop - Establish a feedback loop where staff can report any issues or suggestions regarding the temperature monitoring system, fostering continuous improvement.
By systematically integrating smart temperature sensors into restaurant operations, owners and managers can significantly enhance food safety protocols, improve compliance with health regulations, and streamline day-to-day management tasks. This technological adoption not only safeguards the health of customers but also contributes to the efficiency and reputation of the establishment.
Effortlessly Create, Implement, and Execute Multiple Daily Checklists
Optimize Your Daily Operations with Altametrics
Compliance with Health Regulations through Technology
In the realm of restaurant management, compliance with health regulations is not just a matter of legal obligation but also a crucial aspect of ensuring customer safety and maintaining a reputation for quality. Smart temperature sensors, with their advanced capabilities, play a pivotal role in aiding restaurants to adhere to both local and national food safety regulations.
Food safety regulations, which vary by region, often mandate strict control over the storage, handling, and preparation of food. These regulations typically include specific temperature requirements for different types of food products, especially those stored in refrigerators and freezers. For example, freezer monitoring is essential in ensuring that frozen foods are kept at temperatures that prevent bacterial growth and contamination.
Smart temperature sensors automate the process of temperature monitoring, providing accurate and continuous data. This technology is particularly effective in meeting regulatory requirements in several ways.
1. Continuous and Accurate Monitoring
Smart sensors offer real-time monitoring of temperatures in critical areas like kitchens, storage rooms, refrigerators, and freezers. The continuous data stream from these sensors helps in maintaining the required temperature levels, crucial for compliance with health standards. For instance, freezer monitoring sensors can instantly alert staff if the temperature rises above a safe threshold, enabling immediate corrective action.
2. Automated Record-Keeping
A key component of regulatory compliance is the ability to provide accurate temperature logs during health inspections. Smart sensors automate this process by continuously recording temperature data. This automated record-keeping eliminates manual errors and omissions, providing a reliable and efficient way to maintain records that are essential during inspections.
3. Instant Alerts for Temperature Deviations
Smart sensors can be configured to send instant alerts when temperatures deviate from set thresholds. This feature is vital for prompt response to potential food safety risks, ensuring that issues are addressed before they become critical. This proactive approach to managing temperature-related risks is highly valued in regulatory frameworks.
4. Integration with Compliance Reporting
Many smart sensor systems offer features that integrate with compliance reporting tools. This integration simplifies the process of generating reports for health inspections, making it easier to demonstrate adherence to food safety regulations.
5. Customizable Settings for Specific Regulations
Smart sensors can be programmed to meet specific regulatory requirements of different regions. This customization ensures that restaurants remain compliant with local and national standards, regardless of the varying specifics of these regulations.
The ease of maintaining and reporting temperature records with smart sensors represents a significant advancement in how restaurants manage food safety and comply with health regulations. By leveraging these technological solutions, restaurant owners can not only ensure a higher standard of food safety but also streamline the process of meeting regulatory requirements. In an industry where safety and quality are paramount, the adoption of smart temperature sensors is a strategic step towards maintaining excellence and building trust with customers.
Best Practices for Using Smart Temperature Sensors
The implementation of smart temperature sensors in a restaurant setting marks a significant stride in food safety and operational efficiency. However, to fully harness their potential, it's crucial to follow best practices regarding their placement, maintenance, and the training of staff in their usage and data interpretation.
Optimal Placement of Sensors
1. Strategic Location
Sensors should be strategically placed to ensure accurate readings. For instance, sensors in refrigerators and freezers should not be placed near the door or cooling element, as these areas can give misleading temperature readings. Instead, they should be positioned in areas that best represent the overall temperature of the space.
2. Avoiding Interference
Care should be taken to place sensors where they will not be obstructed by inventory or equipment. Obstructions can interfere with accurate temperature readings and hinder temperature control.
3. Accessibility
While sensors should be out of the way of routine operations, they also need to be accessible for maintenance and calibration checks.
Maintenance of Sensors
1. Regular Calibration
Regular calibration of sensors is crucial to ensure ongoing accuracy. This might involve checking them against a known temperature source and adjusting them as needed.
2. Cleaning and Inspection
Sensors should be kept clean and inspected regularly for signs of damage or wear. Dust, debris, or damage can affect their functionality.
3. Battery Checks
For battery-operated sensors, regular checks and timely replacement of batteries are essential to prevent unexpected failures.
Training Staff
1. Understanding Sensor Data
Staff should be trained in reading and understanding the data provided by the sensors. This includes knowing what normal temperature ranges are for different storage areas and food types.
2. Response to Alerts
Training must also cover how to respond to alerts from the sensors. Staff should know the immediate steps to take if a sensor indicates that a temperature is out of the safe range, such as adjusting the temperature control settings or checking for equipment malfunctions.
3. Incorporating Data into Daily Procedures
Staff should be encouraged to incorporate temperature monitoring into their daily routines and decision-making processes. This includes understanding how temperature data impacts food safety and quality.
4. Reporting and Record-Keeping
Employees should also be trained in the reporting and record-keeping procedures related to temperature monitoring. Understanding how to log data, report anomalies, and maintain records is crucial for compliance and quality control.
By adhering to these best practices, restaurants can ensure that their smart temperature sensors are used effectively. This not only aids in maintaining optimal temperature control but also enhances overall food safety, compliance, and operational efficiency. Training staff to properly use and respond to smart sensor data is integral to leveraging the full benefits of this technology, making it a key component of modern restaurant management.
Embracing Technology for Safer Food Handling
. The integration of smart temperature sensors in the restaurant industry signifies a pivotal shift towards more technologically advanced, efficient, and safe food handling practices. As we have explored throughout this discussion, the benefits of adopting such smart monitoring systems are manifold, addressing key areas of concern for any food service establishment.
The primary advantage of these sensors lies in their ability to provide continuous, accurate temperature monitoring. This feature is crucial in ensuring that food is stored, prepared, and served within safe temperature ranges, significantly reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses. The precision offered by smart sensors goes beyond what traditional manual methods can achieve, offering peace of mind to restaurant owners and managers, knowing that their food handling processes adhere to the highest standards of safety.
Moreover, the automation of temperature monitoring and data logging simplifies compliance with food safety regulations. Smart sensors can record and store temperature data over extended periods, creating an invaluable log that can be referenced during health inspections or audits. This automated record-keeping not only streamlines the compliance process but also reduces the administrative burden on staff, allowing them to focus more on customer service and other operational aspects.
The implementation of smart temperature sensors also contributes to operational efficiency. By providing real-time alerts and enabling remote monitoring, these systems allow for immediate response to potential issues, such as equipment malfunctions or unplanned temperature fluctuations. This proactive approach to managing food safety can save significant time and resources, preventing food spoilage and ensuring consistent quality.
To further optimize your restaurant's task management, consider implementing Altametrics. Altametrics enhances smart temperature sensors in restaurants by offering comprehensive, real-time monitoring of storage facilities, tracking temperature, pressure, humidity, and luminosity. This advanced monitoring eliminates manual checks, freeing staff for other tasks, and ensures consistent adherence to food safety standards. Its alert system enables quick response to any storage issues, minimizing equipment failures and food waste. Altametrics' user-friendly reports on various devices assist in equipment maintenance and staff training, improving operational efficiency and product quality. By integrating with smart sensors, Altametrics helps restaurants maintain high food safety standards, reduce costs, and enhance the dining experience, making it a valuable investment for the industry.
Take Control of Your Operations Team's Tasks
Discover Seamless Workflow Management with Altametrics














